Spring Security 中如何让上级拥有下级的所有权限(案例分析)
答案是能!
松哥之前写过类似的文章,但是主要是讲了用法,今天我们来看看原理!
本文基于当前 Spring Security 5.3.4 来分析,为什么要强调最新版呢?因为在在 5.0.11 版中,角色继承配置和现在不一样。旧版的方案我们现在不讨论了,直接来看当前最新版是怎么处理的。
1.角色继承案例
我们先来一个简单的权限案例。
创建一个 Spring Boot 项目,添加 Spring Security 依赖,并创建两个测试用户,如下:
@Overrideprotected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser('javaboy') .password('{noop}123').roles('admin') .and() .withUser('江南一点雨') .password('{noop}123') .roles('user');}
然后准备三个测试接口,如下:
@RestControllerpublic class HelloController { @GetMapping('/hello') public String hello() { return 'hello'; } @GetMapping('/admin/hello') public String admin() { return 'admin'; } @GetMapping('/user/hello') public String user() { return 'user'; }}
这三个测试接口,我们的规划是这样的:
/hello 是任何人都可以访问的接口 /admin/hello 是具有 admin 身份的人才能访问的接口 /user/hello 是具有 user 身份的人才能访问的接口 所有 user 能够访问的资源,admin 都能够访问注意第四条规范意味着所有具备 admin 身份的人自动具备 user 身份。
接下来我们来配置权限的拦截规则,在 Spring Security 的 configure(HttpSecurity http) 方法中,代码如下:
http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers('/admin/**').hasRole('admin') .antMatchers('/user/**').hasRole('user') .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() ... ...
这里的匹配规则我们采用了 Ant 风格的路径匹配符,Ant 风格的路径匹配符在 Spring 家族中使用非常广泛,它的匹配规则也非常简单:
通配符 含义 ** 匹配多层路径 * 匹配一层路径 ? 匹配任意单个字符
上面配置的含义是:
如果请求路径满足 /admin/** 格式,则用户需要具备 admin 角色。 如果请求路径满足 /user/** 格式,则用户需要具备 user 角色。 剩余的其他格式的请求路径,只需要认证(登录)后就可以访问。注意代码中配置的三条规则的顺序非常重要,和 Shiro 类似,Spring Security 在匹配的时候也是按照从上往下的顺序来匹配,一旦匹配到了就不继续匹配了,所以拦截规则的顺序不能写错。
如果使用角色继承,这个功能很好实现,我们只需要在 SecurityConfig 中添加如下代码来配置角色继承关系即可:
@BeanRoleHierarchy roleHierarchy() { RoleHierarchyImpl hierarchy = new RoleHierarchyImpl(); hierarchy.setHierarchy('ROLE_admin > ROLE_user'); return hierarchy;}
注意,在配置时,需要给角色手动加上 ROLE_ 前缀。上面的配置表示 ROLE_admin 自动具备 ROLE_user 的权限。
接下来,我们启动项目进行测试。
项目启动成功后,我们首先以 江南一点雨的身份进行登录:
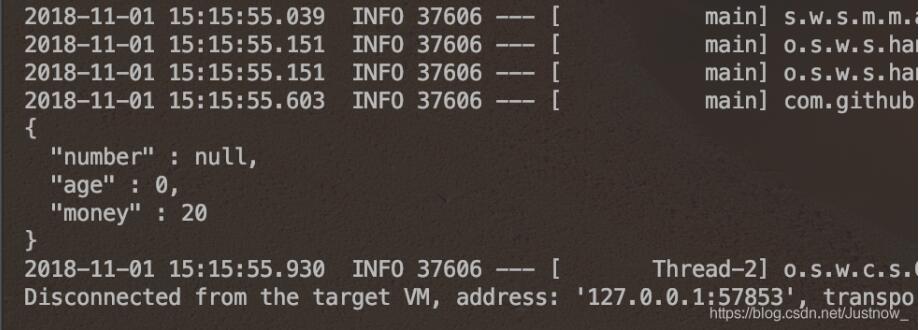
登录成功后,分别访问 /hello,/admin/hello 以及 /user/hello 三个接口,其中:
/hello 因为登录后就可以访问,这个接口访问成功。 /admin/hello 需要 admin 身份,所以访问失败。 /user/hello 需要 user 身份,所以访问成功。再以 javaboy 身份登录,登录成功后,我们发现 javaboy 也能访问 /user/hello 这个接口了,说明我们的角色继承配置没问题!
2.原理分析
这里配置的核心在于我们提供了一个 RoleHierarchy 实例,所以我们的分析就从该类入手。
RoleHierarchy 是一个接口,该接口中只有一个方法:
public interface RoleHierarchy {Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getReachableGrantedAuthorities(Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities);}
这个方法参数 authorities 是一个权限集合,从方法名上看方法的返回值是一个可访问的权限集合。
举个简单的例子,假设角色层次结构是 ROLE_A > ROLE_B > ROLE_C,现在直接给用户分配的权限是 ROLE_A,但实际上用户拥有的权限有 ROLE_A、ROLE_B 以及 ROLE_C。
getReachableGrantedAuthorities 方法的目的就是是根据角色层次定义,将用户真正可以触达的角色解析出来。
RoleHierarchy 接口有两个实现类,如下图:
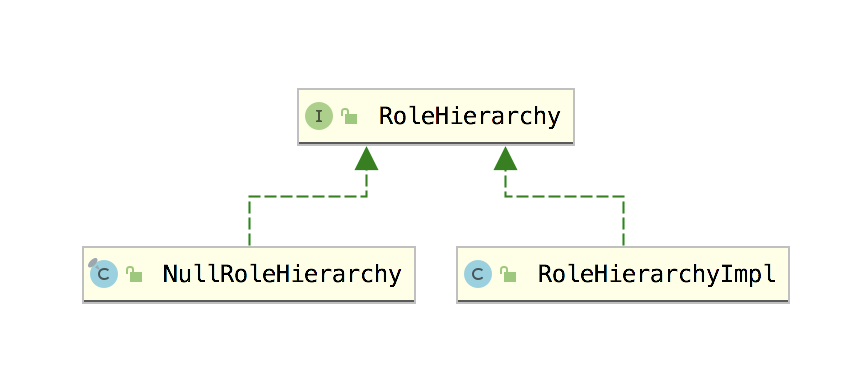
我们来重点看下 RoleHierarchyImpl 类。
这个类中实际上就四个方法 setHierarchy、getReachableGrantedAuthorities、buildRolesReachableInOneStepMap 以及 buildRolesReachableInOneOrMoreStepsMap,我们来逐个进行分析。
首先是我们一开始调用的 setHierarchy 方法,这个方法用来设置角色层级关系:
public void setHierarchy(String roleHierarchyStringRepresentation) {this.roleHierarchyStringRepresentation = roleHierarchyStringRepresentation;if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug('setHierarchy() - The following role hierarchy was set: '+ roleHierarchyStringRepresentation);}buildRolesReachableInOneStepMap();buildRolesReachableInOneOrMoreStepsMap();}
用户传入的字符串变量设置给 roleHierarchyStringRepresentation 属性,然后通过 buildRolesReachableInOneStepMap 和 buildRolesReachableInOneOrMoreStepsMap 方法完成对角色层级的解析。
buildRolesReachableInOneStepMap 方法用来将角色关系解析成一层一层的形式。我们来看下它的源码:
private void buildRolesReachableInOneStepMap() {this.rolesReachableInOneStepMap = new HashMap<>();for (String line : this.roleHierarchyStringRepresentation.split('n')) {String[] roles = line.trim().split('s+>s+');for (int i = 1; i < roles.length; i++) {String higherRole = roles[i - 1];GrantedAuthority lowerRole = new SimpleGrantedAuthority(roles[i]);Set<GrantedAuthority> rolesReachableInOneStepSet;if (!this.rolesReachableInOneStepMap.containsKey(higherRole)) {rolesReachableInOneStepSet = new HashSet<>();this.rolesReachableInOneStepMap.put(higherRole, rolesReachableInOneStepSet);} else {rolesReachableInOneStepSet = this.rolesReachableInOneStepMap.get(higherRole);}rolesReachableInOneStepSet.add(lowerRole);}}}
首先大家看到,按照换行符来解析用户配置的多个角色层级,这是什么意思呢?
我们前面案例中只是配置了 ROLE_admin > ROLE_user,如果你需要配置多个继承关系,怎么配置呢?多个继承关系用 n 隔开即可,如下 ROLE_A > ROLE_B n ROLE_C > ROLE_D。还有一种情况,如果角色层级关系是连续的,也可以这样配置 ROLE_A > ROLE_B > ROLE_C > ROLE_D。
所以这里先用 n 将多层继承关系拆分开形成一个数组,然后对数组进行遍历。
在具体遍历中,通过 > 将角色关系拆分成一个数组,然后对数组进行解析,高一级的角色作为 key,低一级的角色作为 value。
代码比较简单,最终的解析出来存入 rolesReachableInOneStepMap 中的层级关系是这样的:
假设角色继承关系是 ROLE_A > ROLE_B n ROLE_C > ROLE_D n ROLE_C > ROLE_E,Map 中的数据是这样:
A?>B C?>[D,E]假设角色继承关系是 ROLE_A > ROLE_B > ROLE_C > ROLE_D,Map 中的数据是这样:
A?>B B?>C C?>D这是 buildRolesReachableInOneStepMap 方法解析出来的 rolesReachableInOneStepMap 集合。
接下来的 buildRolesReachableInOneOrMoreStepsMap 方法则是对 rolesReachableInOneStepMap 集合进行再次解析,将角色的继承关系拉平。
例如 rolesReachableInOneStepMap 中保存的角色继承关系如下:
A?>B B?>C C?>D经过 buildRolesReachableInOneOrMoreStepsMap 方法解析之后,新的 Map 中保存的数据如下:
A?>[B、C、D] B?>[C、D] C?>D这样解析完成后,每一个角色可以触达到的角色就一目了然了。
我们来看下 buildRolesReachableInOneOrMoreStepsMap 方法的实现逻辑:
private void buildRolesReachableInOneOrMoreStepsMap() {this.rolesReachableInOneOrMoreStepsMap = new HashMap<>();for (String roleName : this.rolesReachableInOneStepMap.keySet()) {Set<GrantedAuthority> rolesToVisitSet = new HashSet<>(this.rolesReachableInOneStepMap.get(roleName));Set<GrantedAuthority> visitedRolesSet = new HashSet<>();while (!rolesToVisitSet.isEmpty()) {GrantedAuthority lowerRole = rolesToVisitSet.iterator().next();rolesToVisitSet.remove(lowerRole);if (!visitedRolesSet.add(lowerRole) ||!this.rolesReachableInOneStepMap.containsKey(lowerRole.getAuthority())) {continue;} else if (roleName.equals(lowerRole.getAuthority())) {throw new CycleInRoleHierarchyException();}rolesToVisitSet.addAll(this.rolesReachableInOneStepMap.get(lowerRole.getAuthority()));}this.rolesReachableInOneOrMoreStepsMap.put(roleName, visitedRolesSet);}}
这个方法还比较巧妙。首先根据 roleName 从 rolesReachableInOneStepMap 中获取对应的 rolesToVisitSet,这个 rolesToVisitSet 是一个 Set 集合,对其进行遍历,将遍历结果添加到 visitedRolesSet 集合中,如果 rolesReachableInOneStepMap 集合的 key 不包含当前读取出来的 lowerRole,说明这个 lowerRole 就是整个角色体系中的最底层,直接 continue。否则就把 lowerRole 在 rolesReachableInOneStepMap 中对应的 value 拿出来继续遍历。
最后将遍历结果存入 rolesReachableInOneOrMoreStepsMap 集合中即可。
这个方法有点绕,小伙伴们可以自己打个断点品一下。
看了上面的分析,小伙伴们可能发现了,其实角色继承,最终还是拉平了去对比。
我们定义的角色有层级,但是代码中又将这种层级拉平了,方便后续的比对。
最后还有一个 getReachableGrantedAuthorities 方法,根据传入的角色分析出其可能潜在包含的一些角色:
public Collection<GrantedAuthority> getReachableGrantedAuthorities(Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {if (authorities == null || authorities.isEmpty()) {return AuthorityUtils.NO_AUTHORITIES;}Set<GrantedAuthority> reachableRoles = new HashSet<>();Set<String> processedNames = new HashSet<>();for (GrantedAuthority authority : authorities) {if (authority.getAuthority() == null) {reachableRoles.add(authority);continue;}if (!processedNames.add(authority.getAuthority())) {continue;}reachableRoles.add(authority);Set<GrantedAuthority> lowerRoles = this.rolesReachableInOneOrMoreStepsMap.get(authority.getAuthority());if (lowerRoles == null) {continue;}for (GrantedAuthority role : lowerRoles) {if (processedNames.add(role.getAuthority())) {reachableRoles.add(role);}}}List<GrantedAuthority> reachableRoleList = new ArrayList<>(reachableRoles.size());reachableRoleList.addAll(reachableRoles);return reachableRoleList;}
这个方法的逻辑比较直白,就是从 rolesReachableInOneOrMoreStepsMap 集合中查询出当前角色真正可访问的角色信息。
3.RoleHierarchyVoter
getReachableGrantedAuthorities 方法将在 RoleHierarchyVoter 投票器中被调用。
public class RoleHierarchyVoter extends RoleVoter {private RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy = null;public RoleHierarchyVoter(RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy) {Assert.notNull(roleHierarchy, 'RoleHierarchy must not be null');this.roleHierarchy = roleHierarchy;}@OverrideCollection<? extends GrantedAuthority> extractAuthorities(Authentication authentication) {return roleHierarchy.getReachableGrantedAuthorities(authentication.getAuthorities());}}
关于 Spring Security 投票器,将是另外一个故事,松哥将在下篇文章中和小伙伴们分享投票器和决策器~
4.小结
到此这篇关于Spring Security 中如何让上级拥有下级的所有权限的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring Security上级拥有下级的所有权限内容请搜索好吧啦网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦网!
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备