手把手教你SpringBoot快速集成Swagger的配置过程
相信大家无论是做前端还是做后端的,都被接口接口文档所折磨过,前端抱怨接口文档和后端给的不一致,后端抱怨写接口文档很麻烦,所以Swagger就诞生了。直接配置即可自动生成接口文档,而且提供了高效的API测试话不多说直接开干导入SpringBoot集成Swagger所需要的依赖
<!--web方便测试--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- swagger2核心包 --> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId> <version>2.9.2</version> </dependency> <!-- swagger-ui 可视化界面 --> <dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId> <version>2.9.2</version> </dependency>
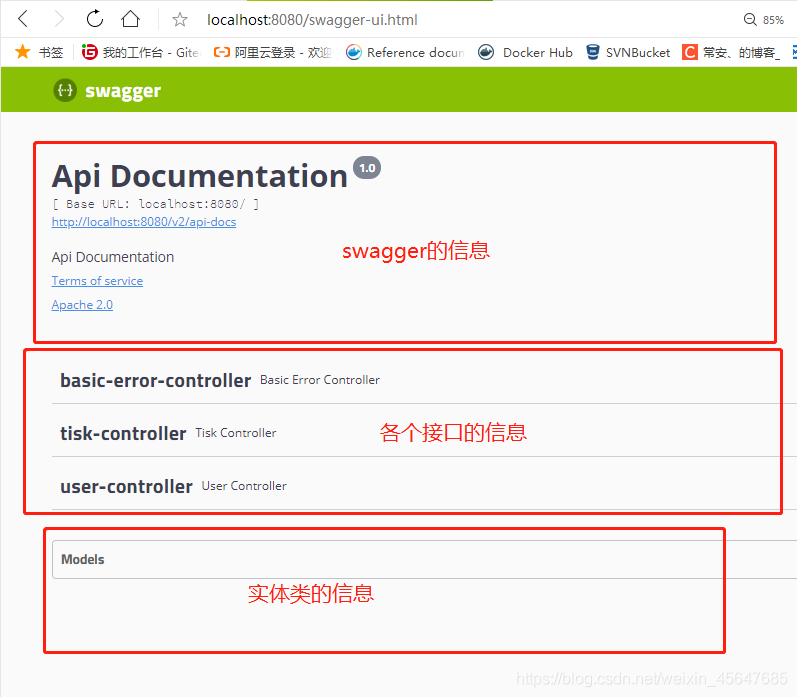
Swagger可视化界面可分为三个区域
Swagger相关配置
package com.example.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;import java.util.ArrayList;@Configuration@EnableSwagger2 //开启Swagger的使用public class SwaggerConfig { @Bean //Swagger的使用主要是要将docket对象传入IOC容器 public Docket docket(){ return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo()) //关于文档的各种信息.enable(true) //使Swagger生效.groupName('常安祖').select()//选择扫描的接口.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage('com.example.controller'))//指定扫描的接口.build(); } public ApiInfo apiInfo(){ Contact contact = new Contact('长安','https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45647685','719801748@qq.com');//个人的联系方式 return new ApiInfo('长安的文档', '长安的开发文档', '1.0', 'urn:tos',null, 'Apache 2.0', 'http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0', new ArrayList());//文档的各种信息 }}
@ApiModel( ) //主要用来标注返回的实体类@ApiModelProperty( ) //主要用来标注实体类中的属性案例:
@ApiModel('用户的实体类')public class User implements Serializable { @ApiModelProperty('用户的id') private Integer id; @ApiModelProperty('用户的姓名') private String name; @ApiModelProperty('用户的年纪') private Integer age; public Integer getId() { return id; } public User(Integer id, String name, Integer age) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; }}
@ApiModelProperty用来标注API接口案例:
package com.yangzihao.controller;import com.yangzihao.entity.User;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@RestControllerpublic class UserController { @ApiModelProperty('得到一个User') @GetMapping('/getUser') public User getUser(){ return new User(1,'测试',18); }}
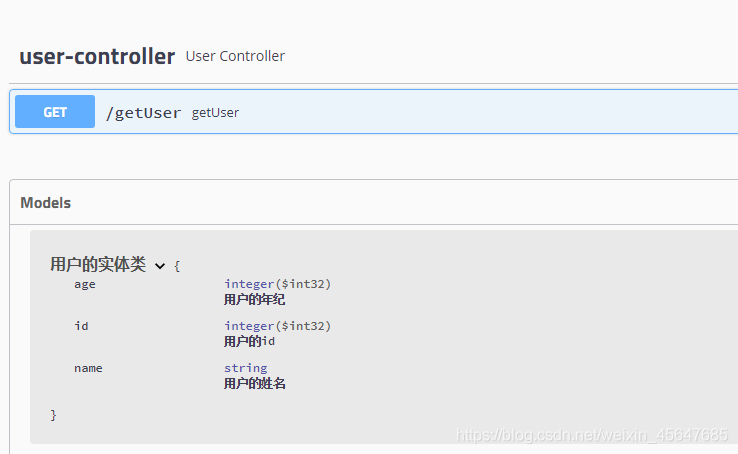
进入Swagger可视化界面
使用Swagger进行接口测试
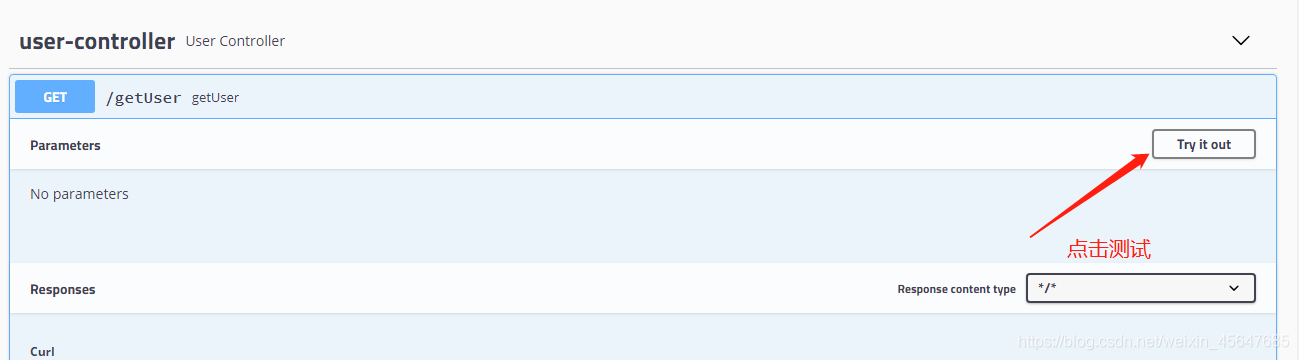
执行
到此这篇关于手把手教你SpringBoot快速集成Swagger的配置过程的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot集成Swagger内容请搜索好吧啦网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦网!
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备